Description of the cloud condensation nuclei counter
General Operation
The CCN instrument consists of a vertical column with wetted walls which provides the water vapor necessary to produce super-saturations. Particles activate into droplets when exposed to the super-saturated conditions. An optical particle counter measures the resulting droplet size distribution. The CCN at several supersaturations is measured using a DMT CCN counter (Roberts and Nenes, 2005). The percent supersaturation (%SS) of the instrument is stepped in 7 intervals every 30 minutes with 5 minutes at each setting in a pyramid form. We use a heat transfer and fluid dynamics model flow model to calculate the %SS (Lance et al., 2006). The model uses the calibrated temperature, pressure and flows in the instrument to calculate the %SS.
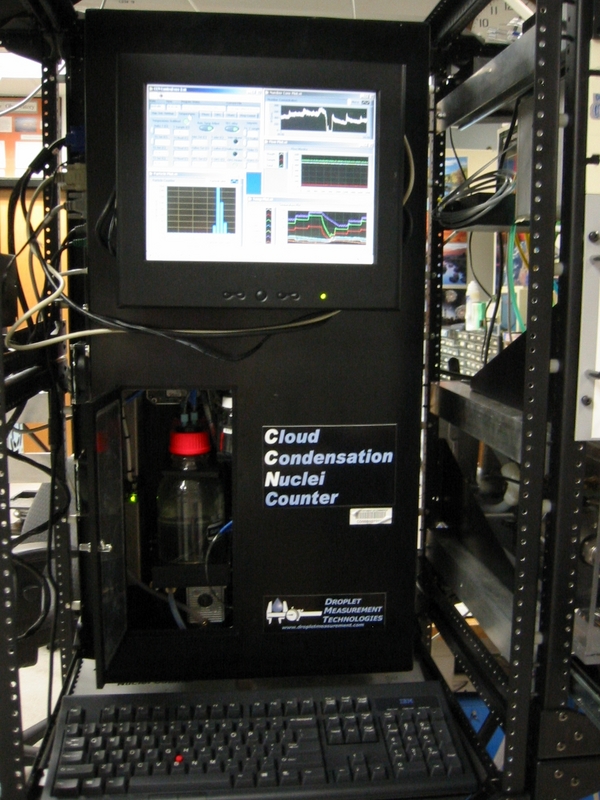

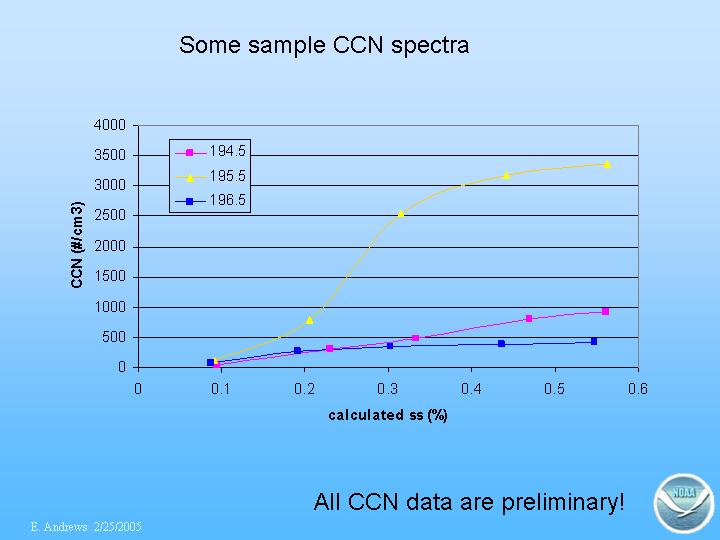
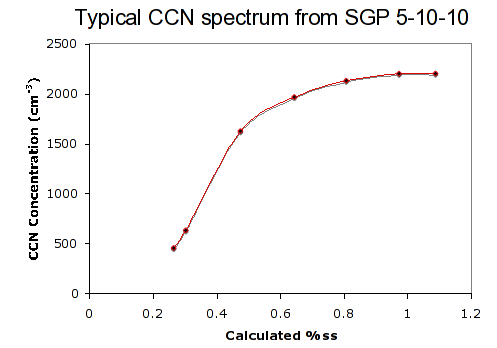
Our CCN instrument comes from Droplet Measurement Technologies (DMT) in Boulder, CO.
References
- Lance, S., J. Medina, J. N. Smith, and A. Nenes, Mapping the operation of the DMT continuous flow CCN counter, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 40(4), 242–254, 2006.
- Roberts, G., and A. Nenes , A continuous-flow streamwise thermal- gradient CCN chamber for atmospheric measurements, Aerosol Sci. Tech- nol., 39(3), 206–221, 2005.
