Aerosol Instrumentation
The individual components for the basic system are described below, along with links to descriptions and pictures of each instrument. A description of an expanded system is provided here. The Aerosol group has also made measurements onboard light aircraft, although those measurements ended in 2009. Go here for information on the Aircraft Aerosol System
Basic Aerosol System
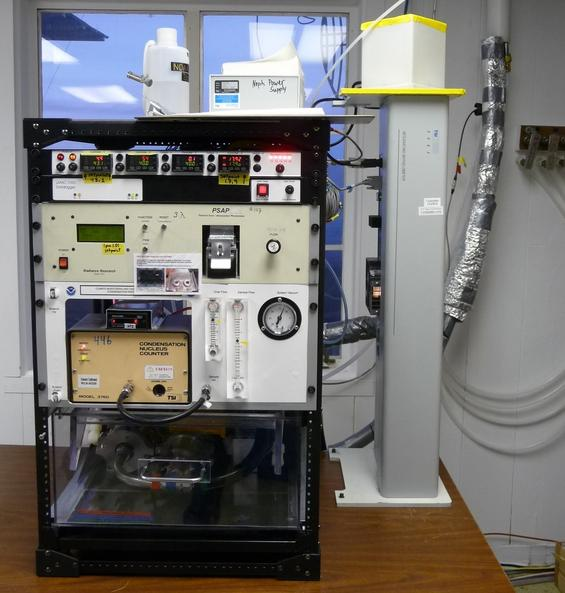
Click on a colored portion of the aerosol system map or on an instrument in the photo to see construction diagrams and images of the instruments and ancillary parts for GML's aerosol system.
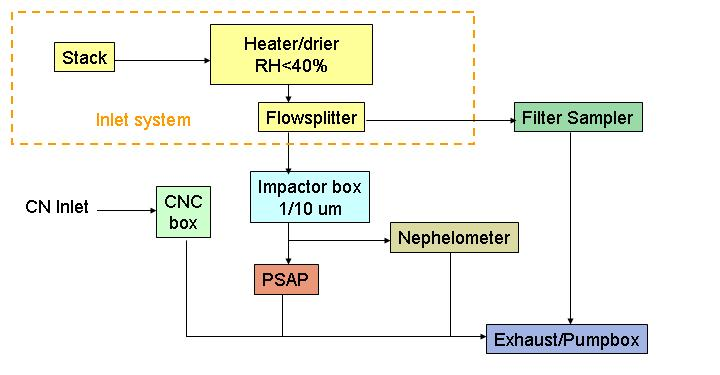

Nephelometers
We use and have used several types of nephelometers. The TSI nephelometer (TSI Model#3563) measures total scattering (between 7 and 170 degrees) and backscattering (between 90 and 170 degrees) by aerosol particles at three wavelengths: blue (450 nm), green (550 nm) and red (700 nm). This instrument, while still in use at most sites, has been discontinued and is no longer supported by the manufacturer.
We are currently testing the Ecotech Aurora 3000 as a replacement at one site and trying to figure out the best way to operate it within our standard instrument system. The Ecotech measures aerosol total scattering and backscattering at three wavelengths (450, 525 and 635 nm) at angles between 9 and 170 degrees (total scattering i and 90 and 170 degrees (backscattering).
The Radiance Research nephelometer (RR Model#903) is a smaller, lighter instrument. It measures total scattering at ~530 nm or ~545nm and we used primarily these on instrumented light aircraft prior to 2009. Prior to ~2000 we also used MsE and MRI nephelometers.
Filter-based absorption photometers
The PSAP (Radiance Research) is a filter-based method that measures light absorption by particles at a single wavelength: green (565 nm) or three wavelengths (467, 530, 660 nm). Particles are collected on a filter and light transmission through the filter is monitored continuously. These instruments (no longer made or supported) were deployed at NFAN sites from the 1990s to the mid-2010s.
The CLAP is a NOAA/GML developed, filter-based method that measures light absorption by particles at three wavelengths (467, 528, 652 nm). The CLAP is similar to the PSAP in that particles are collected on a filter and light transmission through the filter is monitored continuously. The CLAP differs from the PSAP in that instead of a single sample spot, it has 8 sample spots. Solonoids are used to switch to the next sample spot once the transmittance reaches 0.7. Thus, CLAP can run 8x as long as the PSAP before requiring a filter change, ideal for remote sites which aren't visited daily.
We have used various models of aethalometers since the late 1980s, starting with an AE8. Currently AE33 are deployed at several sites. The AE33 is a seven wavelength (370, 470, 520, 590, 660, 880 and 950 nm) instrument. Rather than individual filters, it uses a roll of filter tape that advances when the sample spot has reached a specific attenuation due to loading on the filter.
Condensation Nuclei Counter (CNC)
The aerosol systems in our collaborative network use various types of CNCs to measure particle number concentrations. Particles are drawn into the CNC and vapor is condensed on the particles so that they grow to a size detectable by the instrument optics and thus can be counted.
